Was it Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) or Artificial Intelligence (AI)? If you look beyond the buzzword bingo to correctly interpret the terms, you soon lose track. What exactly do the different concepts mean and how do they distinguish themselves from each other in practice? An overview.
AI, ML and DL demystified
In a nutshell, the situation looks like this:
- AI is the overarching science that deals with the creation of machines that exhibit some form of intelligence.
- Machine Learning is part of AI that focuses on techniques with which computers can learn on the basis of data and patterns.
- Deep Learning, in turn, is the collective name for a group of techniques for self-controlling Machine Learning, where algorithms make themselves smarter.
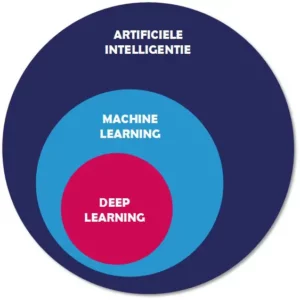
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning thus stand in a hierarchical relationship to each other. In practice, there are of course a few grey areas and many concrete techniques and algorithms can be found at the interface between the various sub-areas. Both AIML and DL have their own history, merits and applications.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is all about building machines that display a certain form of intelligence. As a concept, AI is inextricably linked to the history of the first computers. Let’s go a bit back in time. The Ancient Greeks had already designed a complex analog machine more than two thousand years ago to perform complex astronomical calculations, although their invention was still far removed from contemporary views on artificial intelligence.

The British mathematician and code cracker Alan Turing is generally regarded as the father of the modern computer. His pioneering work in the 1940s and 1950s not only heralded the era of lightning-fast calculators. Turing also laid the philosophical and practical basis for abstract concepts such as the self-awareness of intelligent computers. That groundbreaking thinking eventually led to the Turing test, which still constitutes an important, if somewhat outdated, measure of whether or not a machine can be considered intelligent and self-thinking.

Today, AI includes a wide range of different concepts, which include Machine Learning and Deep Learning. In the meantime, a lot of work is also being done on practical implementations of fully conscious artificial intelligence, which means that the field will soon be expanded with, for example, human AI.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is part of AI that focuses on methods with which computers can learn based on data and patterns. In practice, this is done with the help of data mining. This is a technique for extracting relevant information from databases. An algorithm for Machine Learning does not need a structured database for this – such as an Excel file with neatly ordered data – but is smart enough to decipher relevant data points based on unstructured data. Many companies already apply Machine Learning today. Just think of Amazon, which automatically recommends its users products based on their previous purchases. Another example is Netflix, which proposes series and films to its subscribers on the basis of earlier viewing behavior.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is essentially an advanced form of Machine Learning with one important distinguishing feature: independent adjustment. A Deep Learning model can adjust itself on the basis of external signals – that is, data -, where Machine Learning can only adjust on the basis of manual adjustment, such as in the underlying code of the algorithm.
Well-known examples of Deep Learning are found today in self-driving cars and in our own Trendskout platform. Neither of them requires explicit user feedback to adapt successfully. Deep Learning algorithms are fully focused on the requested end result and adjust themselves accordingly.
Neural networks are often confused with Deep Learning, but they are not the same. A neural network is a technique that can be used for Machine Learning, Deep Learning and overarching AI. Neural networks simulate the functioning of the human brain to classify information based on examples. For example, as a way to quickly categorize images based on a limited set of photos.
Conclusion: Appropriate type of AI for each project
We admit: sometimes confusing terminology and the constantly changing AI landscape do not make it easier to see the forest for the trees. Using the right technology in an organization is specialist work. That is exactly where the Trendskout platform proves its value. The platform automatically chooses the appropriate AI algorithm for each business case based on the relevant parameters.

